The lungs, bronchi, trachea, and other airways are all susceptible to a variety of disorders that collectively make up the respiratory system. Depending on the severity of the sickness, these conditions can drastically reduce a person’s standard of living. The air we breathe, cigarette smoke, viruses, allergies, and even our genes can all play a role in their development. Learn about the signs, symptoms, causes, and ways to avoid several common respiratory disorders with this comprehensive guide.
Acquiring Knowledge About Respiratory Illnesses
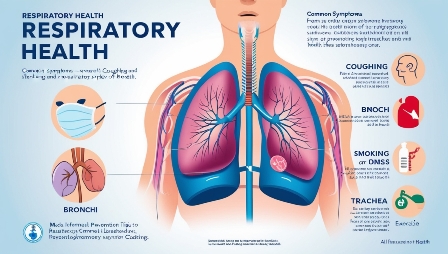
Breathing is made possible by the respiratory system, which also supplies the body with oxygen. Vital organs that oxygenate blood are the lungs, which are part of this system.
The airway that carries air to the lungs is called the bronchial tube.
– The windpipe that carries air from the nasal passages and oral cavity to the lungs is called the trachea.
The diaphragm is a muscle that helps with breathing by allowing the lungs to contract and expand.
Symptoms including shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing, and generalised exhaustion can develop when the respiratory system is compromised. We will go over the most prevalent respiratory illnesses.
Classification of Respiratory Illnesses
1. Asthma
Synopsis: In asthma, the airways are irritated and narrowed over time, which makes breathing difficult. Things in the environment or allergens can set it off.
– Root Causes: Dust mites, mold, pollen, smoking, and animal dander are allergic asthma triggers. Exercising, being under stress, or being cold can all amplify symptoms.
– Signs and symptoms: Coughing up mucus, wheezing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing are common signs and symptoms.
– Treatment: While there is currently no cure for asthma, it can be controlled with medicine (such as inhalers), behavioral modifications, and avoiding things that trigger attacks.
2. COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
COPD is a chronic inflammatory disorder that worsens with time and causes airflow obstruction in the lungs. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are the two primary diseases that fall under this umbrella.
– What causes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)? Smoking, of course, but environmental toxins and occupational dust are also factors.
Signs and symptoms: Difficulty breathing, a persistent cough that produces mucus, recurrent respiratory infections, and extreme exhaustion.
– Medications: bronchodilators, steroids, lifestyle changes, and, in severe instances, oxygen therapy are all part of the treatment plan.
3. Bronchitis
General Information: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which lead air to the lungs, is known as bronchitis. This can have a short-term or long-term duration.
Infections with viruses or bacteria are common causes of acute bronchitis, whereas smoking and long-term exposure to pollutants are the most common causes of chronic bronchitis.
– Signs: Difficulty breathing, wheezing, mucous production, and a persistent cough.
– Treatment: Getting plenty of sleep, drinking enough of water, and, in severe cases, antibiotics to kill any bacteria. Bronchodilators and behavioral modifications are suggested for long-term instances.
4. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that can cause inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. If left untreated, the sacs can fill up with fluid or pus.
The most frequent bacterium that can cause this condition is Streptococcus pneumoniae, however viruses such as influenza and fungi can also play a role.
– Signs: Chest pain, fast breathing, high temperature, chills, and a cough that produces phlegm are symptoms.
– Treatment: Prophylactic antibiotics against bacteria, antivirals against viruses, and supportive care are all part of the management plan for pneumonia. Some forms of pneumonia can also be prevented with vaccination.
5. Lung Cancer
Overview: Tumors arising from uncontrolled growth of aberrant cells in the lungs constitute lung cancer. On a global scale, it ranks high among cancer killers.
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer, however environmental toxins, genetic predisposition, and secondhand smoke can also cause the disease in nonsmokers.
Signs and symptoms include a persistent cough, blood in the mucus, unexplained loss of weight, difficulty breathing, and chest discomfort.
– Care: Surgical excision, chemo, radiation, and targeted medication therapy are all viable treatment choices. Finding issues early on greatly enhances the quality of treatment.
6. Tuberculosis (TB)
General Information: The Mycobacterium tuberculosis germs cause tuberculosis, an infectious disease that mostly affects the lungs but can spread to other organs.
Reasons: When a person with tuberculosis coughs or sneezes, the virus is able to spread through the airborne droplets.
Fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, fever, and a persistent cough are some of the symptoms.
Treatment for tuberculosis (TB) typically involves a lengthy regimen of medications. Controlling its spread requires prompt treatment and vaccination.
Methods for Avoiding Respiratory Illnesses
The key to lowering the risk of respiratory disorders is prevention. Here are a few practical steps:
1. don’t light up. Tobacco usage is directly linked to a host of respiratory illnesses. To lessen one’s chances of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer, one should quit smoking and stay away from those who smoke.
2. Reducing Pollutant Exposure: A mask in polluted places, an air purifier at home, and less exposure to harmful chemicals, fumes, and dust can all contribute to a healthy respiratory system.
3, get some exercise on a regular basis; doing so will help your lungs and respiratory system work better. Lung capacity can be improved through aerobic exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking.
4. Practice Good Hygiene: To reduce the risk of respiratory diseases such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and tuberculosis, it is recommended to regularly wash hands, use hand sanitizers, and stay away from ill people.
5. Immunization: Vaccines help protect against certain respiratory infections, such as influenza and pneumonia. This is particularly true for vulnerable populations like children, the elderly, and those with impaired immune systems.
6. Eat Well: Maintaining healthy respiratory function is possible with a well-balanced diet that is high in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C, and vitamin E. To keep your lungs healthy, eat plenty of citrus fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fatty fish.
7. Keep Stress at Bay: Respiratory health can be adversely affected by chronic stress. Mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation practices can aid in stress management and immune system support.
In summary
Millions of people around the world suffer from respiratory illnesses, which have a negative effect on their health and quality of life. People can take charge of their health and reduce their risk of respiratory diseases by learning about them and being familiar with their symptoms, types, and causes.
Reducing the chance of acquiring respiratory disorders is possible by changes in lifestyle, preventative treatment, and avoiding harmful exposures. go medical help right away if you notice any symptoms so you can go on the road to recovery.
A healthy respiratory system is a key component of a healthy body, and there are simple things you can do now to safeguard your health tomorrow.